Advanced Horizontal Analytical Model
This model simulates the pressure response in a horizontal well within a rectangular-shaped reservoir with anisotropic heterogeneities (i.e., differences in permeability in the x, y, and z directions), or dual-porosity characteristics. The anisotropy is handled using a conformal mapping procedure that adjusts the boundary sizes accordingly to mimic the effect of increased or decreased permeability in each direction. The horizontal well is oriented in the x-direction, and may be at any location within the reservoir (see figure below) and supports no-flow boundaries.
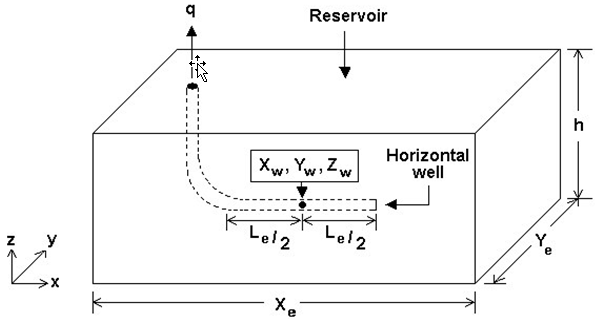
Note that the effective wellbore length (Le) defines the wellbore area open to fluid flow. The cylindrical source solution is used at very early times, which is followed by Green’s function solutions for horizontal wells, as developed by Thompson et al. (1991). No-flow boundaries are modeled using the method of images. The result is superposed in time based on the rate history provided. The following flow regimes can be handled by this model:
- Wellbore storage
- Vertical radial flow
- Linear horizontal flow
- Elliptical flow
- Horizontal radial flow
- Boundary effects
- Pseudo-steady state flow