Gas Condensate Properties
Assume reservoir gas enters the wellbore. On the way to surface and in the separator, the pressure and temperature decrease. The heavier components drop out of the gas in the form of liquid condensate. At the surface, we measure the gas rate and monitor the condensate volumes. We are interested in using the sandface gas rates in the analysis, so we recombine the condensate monitored at the surface into gas.
Based on the gas properties, Condensate Gas Ratio (CGR), Condensate Gravity (gcnd), Separator Temperature (Tsep), and Separator Pressure (psep), a Recombined Gas Rate Factor (RGRF) and Recombined Gas Gravity (gr) can be calculated. The measured gas rates are multiplied by the RGRF to get the total sandface rate. The gas at sandface is richer than the gas at surface, so the higher Recombined Gas Gravity is used for analysis. In WellTest, you can either use a constant RGRF calculated in Gas Properties, or calculate a different RGRF for each rate based on the current CGR on the Production Editor tab.
In general, if the CGR < 12 bbl/MMscf, using Recombination isn’t necessary.
| Note: | The condensate is separated from the gas in the separator and measured in the stock tank. However, the fluid in the stock tank has been flashed and will no longer contain components < C5. |
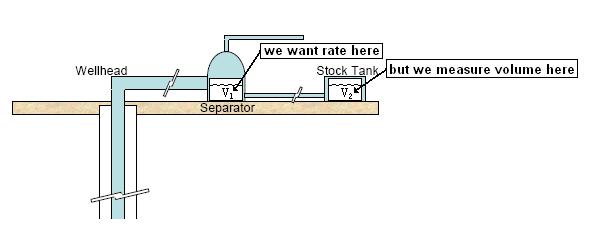
V2 < V1, we want V1 (q1)
q1 = q2 / shrinkage factor (0.7 – 0.9)
Therefore, it is important to divide the condensate rates by a shrinkage factor (usually between 0.7 - 0.9) to get the correct condensate rate used to calculate the CGR. The shrinkage factor could be determined from a flash calculation.