Fracture Properties
Subtopics:
Fracture Flow Capacity (kfwf)
Fracture flow capacity is a measure of how conductive, or how easily fluid moves through a fracture. It is defined as the product of fracture permeability and fracture width (kfwf) as shown below.
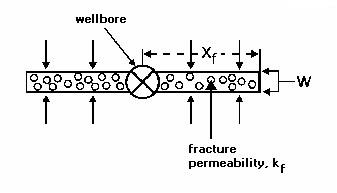
A large value of fracture flow capacity (>10,000 md ft) represents an infinite conductivity fracture, and yields a linear fracture flow response on the derivative. A small value of the fracture flow capacity (<10,000 md ft) represents a finite conductivity fracture and may yield a bilinear fracture flow response on the derivative. When the value of fracture flow capacity is divided by the product of formation permeability (k) and fracture half-length (Xf), the result is known as the dimensionless fracture conductivity (FCD) defined as:
| Note: | This dimensionless form is a more common measure of fracture conductivity that is found in the literature. |
Fracture Half-Length (Xf)
A hydraulic fracture is typically modeled by assuming it extends in a straight line equally on each side of the wellbore, as shown below:
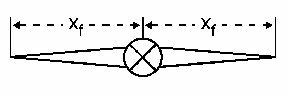
As shown, the fracture half-length is the distance from the well to the tip of the fracture.
The fracture half-length depends on the size of the fracture treatment and varies from a few feet to a few hundred feet. In pressure transient analysis, it is estimated from the linear fracture flow analysis.